Among the different functions, vitamin D is important for little growing bodies as it assists with the absorption of calcium and helps grow strong bones and teeth. Vitamin D also plays a role in maintaining your little ones muscle function.
But not only that, actions of vitamin D have emerged that go beyond bones, teeth and muscles. In fact, vitamin D also plays a supportive role in the functioning of the immune system in children and adults.
Adequate vitamin D is therefore very important in all age groups. In particular, it is so in the first years of life, when babies and children are experiencing rapid periods of growth.
Unlike other vitamins, only a small amount of Vitamin D comes from our diet. Foods, in general, are low in vitamin D, apart from some, mainly of animal origin, such as salmon, sardines, and eggs. Among the vegetable sources, mushrooms can be mentioned. In any case, both animal and vegetable sources are consumed in limited quantities by babies starting on solids, and through their toddler years. It is not easy to consume the right amount of vitamin D from the diet alone.
Vitamin D is quite a unique vitamin as it can be produced directly by our body through exposure of the skin to direct sunlight. In fact, most of it is produced in this way. This is quite a dilemma given the precautions we all take to avoid the harmful effects of the sun’s ultraviolet rays. It’s understandable that babies and toddlers may have very limited exposure to direct sunlight and therefore may be at risk of not getting enough Vitamin D.
The production of vitamin D in the skin occurs when you are exposed to direct sunlight, however the recommended period of exposure will vary depending on where you live, the season, time of day, and even cloud cover.
- Across Australia, it’s safe to go outside without sun protection if the UV index is below 3. For most places, this will be early morning and late afternoon all year around. In the more southern parts of Australia (e.g. Melbourne, Hobart, Adelaide) this will likely be all of the day through winter and parts of Autumn and Spring.
- For most parts of Australia, a few minutes a day of regular incidental sun exposure, most days of the week, should be enough to maintain Vitamin D levels.
- The skin production of vitamin D is also influenced by other factors, such as dark skin pigmentation or the use of sunscreens, which reduce its production.
Considering sun protection is highly recommended when the UV index is above 3, and exposing children to the sun during the hottest hours of the day is not recommended, the sun, alone, may not be enough to meet a child’s vitamin D requirement.
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, approximately 1 in 4 women in Australia are Vitamin D deficient. Pregnant mums who are Vitamin D deficient are likely to pass this on to their baby.
Vitamin D deficiency can be much higher, as many as 1 in 2 people, in the south-eastern states during winter (Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania).
Australian data on infants Vitamin D status is more difficult to find, with one report showing over 50% of infants (40% insufficient, 11% deficient) have lower than recommended levels of Vitamin D.
It can be very difficult for infants and children to achieve adequate Vitamin D intakes for various reasons, including:
- Breast milk is naturally low in Vitamin D.
- Exposure to direct sun is often restricted in early life.
- Vitamin D-rich foods (e.g. Oily fish, egg yolks, organ meat) are not commonly consumed regularly in early life.
- Vitamin D supplementation may be necessary to help ensure adequate Vitamin D status in infants and toddlers. If you are unsure, chat to your healthcare professional.
There are currently no national vitamin D supplementation guidelines specifically for Australia. However, several Australian hospitals and community health departments do have specific supplementation advice for infants on their websites.
In Australia, and globally the recommended level of vitamin D supplementation for infants is 400 IU (International Units) per day and 1000IU per day for pregnant women.
Please consult your health care professional regarding Vitamin D supplementation for you or your baby.
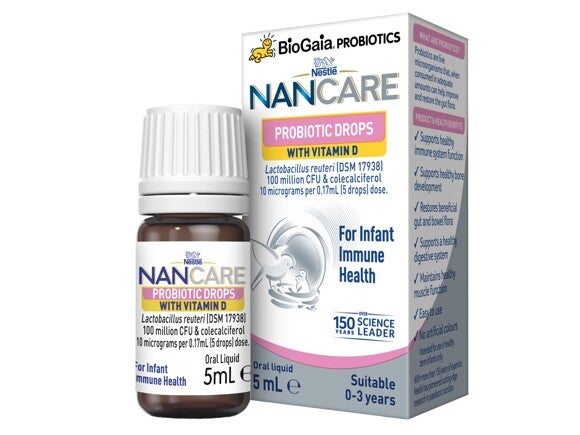
With 400 IU of Vitamin D per dose (5 drops), NAN CARE Probiotic Drops with Vitamin D can help ensure adequate Vitamin D status in infants and children, promoting healthy bone development and immune system function.
NAN CARE Probiotic Drops with Vitamin D is a convenient supplement that also contains probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938), supporting a healthy, balanced gut microbiota in the digestive system.
Features and benefits:
- Supports healthy immune system function
- Supports healthy bone development
- Restores beneficial gut and bowel flora
- Maintains healthy muscle function
- No artificial colours
- Convenient 5 drops dosage taken once daily
- No need to refrigerate
Always read the label and follow the directions for use.
With probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 helping restore the balance of bacteria in the digestive system. NAN CARE Probiotic Drops with Vitamin D is a convenient supplement with probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri (DSM 17938) supporting a healthy, balanced gut microbiota and vitamin D promoting healthy bone development and immune system function.
Sources
Healthdirect Australia - https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/vitamin-d-deficiency
Cancer Council - https://www.cancer.org.au/cancer-information/causes-and-prevention/sun-safety/vitamin-d
Australian Bureau of Statistics - Vitamin D | Australian Bureau of Statistics (https://www.abs.gov.au/articles/vitamin-d)
